Phlox: planting and care in the open field
Content:
There are many legends about phlox. Flowers in them awaken passions, make you love and hate, feel keenly and intensely. They say that they will definitely bring happiness if you grow them with your own hands. And traditional healers advise drinking a decoction of white phlox petals in order to always be collected and calm.
Description of the plant
In culture, about 40 species of phlox are grown as annual or perennial beautifully flowering herbs and shrubs. They belong to the Polemoniaceae family. The Swedish botanist K. Linnaeus, who was engaged in the 18th century. describing wild flowers, he gave them the Greek name φλόξ, comparing it to a bright flame.
Flower inflorescences are collected in various configurations - panicles, pyramids, cones. Plants have strong stems, erect, recumbent or ascending, with a height of 30 cm to 1.8 m. Strongly branching roots penetrate deep into the soil. Due to this, perennial phloxes tolerate wintering well in the open field. Some phlox species bloom from early spring, mid-summer phlox blooms, belonging to mid-flowering plants, in August, the turn of late species comes.
What you need to know about phlox breeding
Many growers do not classify phlox as plants with which there may be some difficulties in reproduction. After all, these flowers, with an attentive attitude to the matter, can be bred in several ways, and all of them give positive results.
Seed propagation
This method is used by breeders to grow plants with new characteristics, as the color and shape of the inflorescences change. Seeds are harvested from ripe fruit pods and in the same year in September-November they are sown in containers, which are dropped in the garden for the winter. During the winter, the seeds undergo stratification (sleep in the cold), germinate in the spring. Seedlings are transplanted into the soil when the plants reach a height of 8-10 cm.
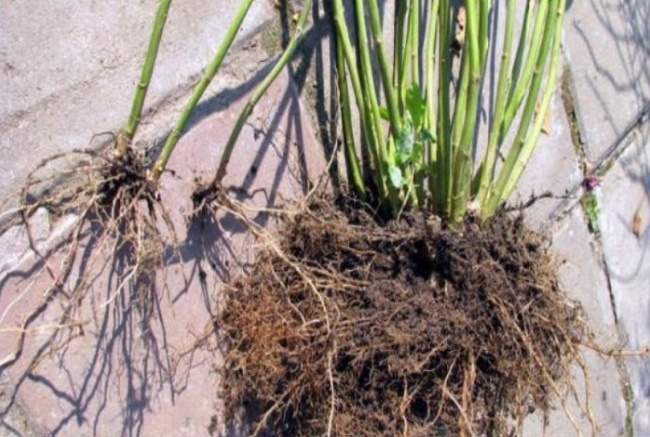
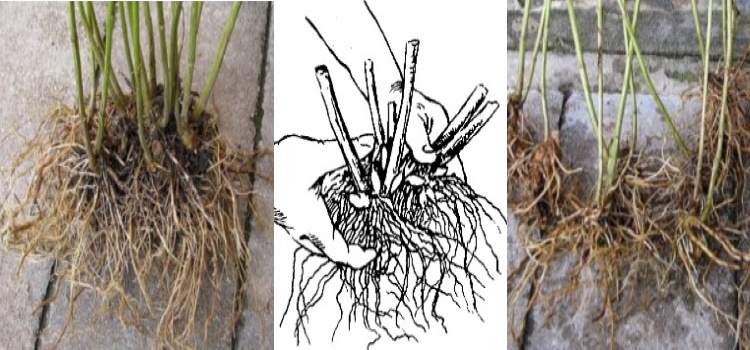
Dividing the bush
The method of dividing the bush is used either in the spring at the beginning of the development of the bush, or in early autumn. Thus, plants are propagated at the age of 5-6 years, having well-branched large roots. Phlox rhizomes are dug out together with a clod of earth, which will protect the plants from severe damage. Then the earth must be shaken off and carefully separate the root collars going to different stems from each other.
Each new part should have eyes, shoot rudiments and several root processes. Separated bushes are best planted in the ground immediately. If this is not possible, then prepare a clay chatterbox. The strips are kept in it for 3-5 minutes. and placed in a plastic bag or sprinkled with damp earth, this will allow the roots to not dry out.
Propagation by cuttings
For the formation of cuttings, shoots without signs of disease, traces of pests, or just phlox leaves are used.Shoots and leaves should be well developed and cut from healthy plants. In the spring, before the beginning of budding, the method of stem cuttings is used; in the summer, propagation is carried out with the help of leaves, which are cut off together with the axillary bud on a small piece of the stem. The leaves are planted in moist soil mixed with sand and vermiculite to a depth of 1.5-2 cm. The axillary bud and stem should be in the substrate. The boxes with cuttings are covered with glass, which is lifted and moistened daily.
For stem cuttings, green, strong shoots are chosen and only from healthy plants. The shoots are cut into several parts so that each one has four leaves located opposite each other, that is, two nodes. Above the upper leaves, 2 cm of the stem is left, the lower cut is made directly under the knot. The upper leaves are completely removed, the leaves of the lower node are cut in half. The cuttings are rooted in fertile soil. Use seed boxes or open field trenches. Plants create greenhouse conditions.
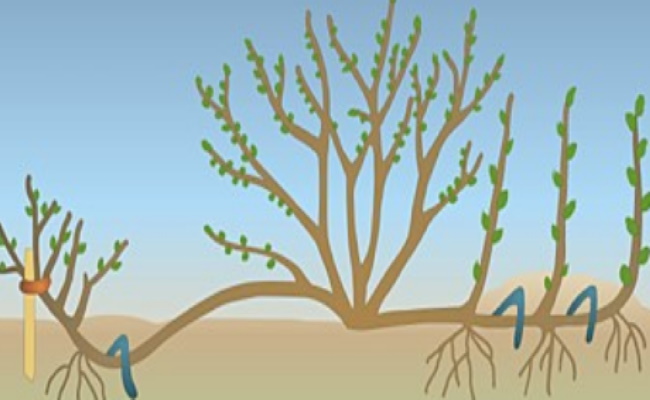
Reproduction by layering
This method is very simple. It is most often used to grow new perennial phlox. The lower parts of the plant are covered with moistened soil at 1/3 of the height of the bush. The earth is constantly moistened. When roots appear on the stems, the layers are freed from the soil, cut off from the bush and planted in a permanent growing place.
How to choose the right landing site
Among the various phloxes, there are still a lot of wild species. One of them grows in Siberia, this mountain flower is named after the place of origin - Phlox Sibirica. This fact once again emphasizes how unpretentious phloxes are, planting and caring for them in the open field does not require much effort, material costs and some impossible conditions.
Kidney requirements
The soil in the flower garden should be fertile and light with a neutral level of acidity. If necessary, lime and sand are added to the planting holes for deoxidation. To increase fertility, peat, mineral fertilizers, highly diluted slurry, compost are used.
Influence of sunlight
Phloxes really need sufficient lighting. Only on well-warmed areas of the earth, phloxes will have powerful roots, and bright sunlight will accelerate the processes of photosynthesis, prevent the stems from becoming thin and elongated, and allow plants to tie dense large inflorescences of bright colors.
Temperature
All types of phlox (both annuals and perennials) do not like shade, in it they form small loose inflorescences, but they tolerate heat well. Phlox bloom until late autumn - before frost. Mild freezing temperatures will cause the plants to shed their flower petals, but the phlox stems will remain green.
Air humidity
The increased dryness of the air will have little effect on the appearance of flowering shrubs, if the roots of the plants do not suffer from a lack of moisture. In this case, scorch marks may form on the leaves, because phlox grow wild where there is a lot of light and moisture. To make the flowers in the garden comfortable, maintain an average level of humidity, if necessary, surface spraying of plants is carried out.
How to plant
Planting conditions depend on the climate of the growing site. Phloxes are cold-hardy crops, so they are popular in areas with different climates and day lengths. In regions with long cold seasons, phlox are not grown on the northern sides of the plots and in the shade.
In places with a sharply continental climate, early varieties with short growing periods are used for cultivation. In the Urals, for planting and caring for phlox in the open field, the southern hills are taken away, protected from the winds. In the southern regions, slightly shaded places are allocated for phloxes, available for watering and regular maintenance.
How to care for phlox
Like all cultivated plants, phloxes cannot do without the active participation of humans in their lives.
How to feed
The first top dressing is necessary in early spring, after winter shelters - foliage, dry grass or artificial protective materials - have been removed from the soil surface. For the growth of stems and the formation of buds, nitrogen fertilizers will be needed: saltpeter, urea or feeding with chicken droppings, mullein. In summer, plants need superphosphate, boron and potassium magnesium for abundant flowering. In autumn, potassium sulfate and phosphorus fertilizers are used.
Loosening and mulching
The root soil crust, formed after rains and watering, does not allow the roots of the plant to breathe normally, and the cracked earth dries them out. Therefore, one cannot do without loosening the soil when caring for phlox. To simultaneously loosen the soil and remove weeds, flat cutters and hoes are used.
Mulching the root zone in the summer allows plant roots not to suffer from overheating and lack of moisture, and the soil does not dry out. Natural and artificial materials are suitable for mulch: cut grass, last year's sawdust, dried bark, decomposed compost without seeds, stone, sand, gravel, special plastic.
Pruning and shaping the crown
For better tillering of phloxes, pinch over the fifth pair of leaves. At this time, the plants should have well-developed stems and at least six leaf nodes. The pinching is carried out before the formation of buds. As a result, lateral shoots grow, the flowering zone increases, the crown of the bushes expands. As flowering proceeds, dried flowers are removed from the inflorescences.
In areas with severe winters, pruning of dying stems in early phlox species begins at the end of August, late varieties are pruned in October-November. The work is carried out with sharp tools so that the stems do not grind. In order not to harm the renewal buds, ten-centimeter stumps are left.
Watering
The powerful root system of phlox is able to raise a lot of moisture to the tops of the plants, but it is necessary that this moisture be in the soil. The need for watering and their intensity are determined by the appearance of the plant: with a lack of moisture, the lower parts of the stems turn pale, the leaves turn yellow and die off, the inflorescences become smaller. When the soil dries up per 1 m², up to two buckets of water are used, it is necessary that the moisture soaks the ground to the layer where the roots are located.
Wintering and shelter
In cold climates and in those places where there is little snow in winter, but frosts are fierce, cut bushes of plants are covered with dry peat and fallen leaves. The thickness of the shelter is up to 10 cm. In the spring, the protection is removed. Where phloxes are not pruned in autumn, snow accumulates in the bushes and becomes an additional plant protection.
When to transplant phlox
For transplanting phlox, the most favorable period is autumn two to three weeks before the expected frost. By the time of transplantation, the stems of phlox should already be cut off, and the soil is not very hot. A spring transplant is carried out after the snow melts and the ground thaws. In the summer, transplants are carried out by dividing the bush during the entire warm season.
Pest and disease control
Phloxes suffer from viral and fungal diseases and leaf-eating insects. You have to fight them and take care of flower bushes all the time until the plants go into hibernation. To destroy pests and various pathogens, a variety of chemical and biological agents are used; decoctions and infusions based on folk recipes are used to scare away insects.
Phlox are very beautiful flowers.To plant them on your site, it is enough to love plants and be able to care for them.