Orchid peduncle: causes of diseases and methods of dealing with them
Content:
Houses are engaged in the cultivation of orchids so that they bloom beautifully and delight the owners. Sometimes the onset of the decorative period is delayed. In addition, inexperienced growers confuse flowering shoots with air roots or babies. It is useful to know what an orchid peduncle is and how it appears. If a flower stem is being formed, it is valued to create the ideal conditions for proper care and growth. The appearance of flowers will not keep you waiting.
Reasons for the appearance
The elongated flexible shoot, where the buds are formed, is called the peduncle. One flower arrow holds 10-50 buds. When the previous stem is cut not to the base, but to the dormant bud, it will release a peduncle in the fall. Flowers will form on it in a month and a half.
An arrow warns of imminent flowering. Its height is 80-100 cm under suitable growing conditions. Its formation means the flowering process: buds appear that grow, develop, open. The flower shoot is involved in the formation of inflorescences, saturates them with moisture and nutrients.
The flowering phase lasts an average of 3 months. The flower arrow is involved in reproductive function. If perfect care is carried out, the formation of children occurs on the breakthrough flowering process. When the buds have faded, their germination begins. They are held on the peduncle until they are fully formed.
What does it look like
The flower shoot varies greatly throughout life. There are 2 types: old and newly formed. A young peduncle grows out of the bosom, where the leaf comes close to the shoot. It is characterized by:
- intense green or light green color;
- growing to the side or up towards the sun;
- smooth shape with a sharp tip.
The young flower stem is covered with scales. 2 months is the period when the buds will open. After a certain time, the flowering arrow is improved and modified, turning into a juicy, elongated and flexible shoot. Buds will open on it.
After flowering, the orchid looks different: the green color changes to brownish yellow. Sometimes there are red, deep purple shades.
After that, the old bud dries up and falls off. It is useful to cut off the stem when the last bud is withered. The procedure will keep the orchid strong. The end of the peduncle signals the flowering phase. A green bud indicates the possibility of growth and budding.
A yellow, blackened, dry tip indicates the end of flowering. The flower grower decides on his own about the need to cut the flower-bearing arrow. Old peduncles lead to a weakening of flower growth and a delay in the formation of new shoots. But the old flower stem forms babies and is able to bloom again.
How many peduncles can there be
The plant does not release more than 3 flower stems.Usually there is 1 shoot with blossoming flowers. The age of the culture and the presence of 8-10 leaves in the outlet are conditions when 2 or 3 peduncles are formed, causing stress in the orchid. Often, active flowering is accompanied by a weak culture. The creation of suitable conditions by experienced florists causes the appearance of 2 peduncles on the orchid.
How to distinguish from other parts
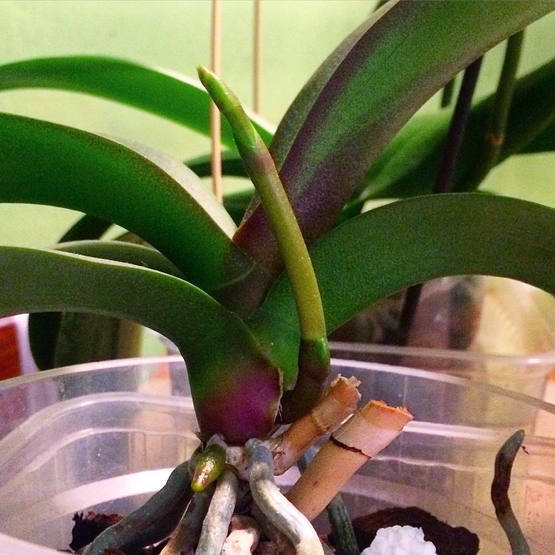
In orchids, flower shoots are shoots that form below in the aboveground area and grow upward. If a peduncle is formed, flowers open on it. The emerging shoot is often confused with roots or epiphyte babies due to small differences.
Emphasis is placed on the following manifestations in order to establish where the orchid has a peduncle, children and root:
- the shape of the flowering shoots is conical, the roots are rounded;
- the tip of the flowering arrow, when growing up, resembles a boat;
- the central vein of the leaf is the place where the flower shoot is formed;
- arrow formation occurs where flowering previously occurred;
- the main difference between the flower shoot and other areas of the culture is the buds.
The peduncle is covered with irregularities in the form of scales or small thorns, which are dormant buds.
The flower stem is responsible for the gracefulness of the orchid - the formation of buds and the blooming of flowers are noted on it. At the top is the green tip, which represents the growth point. New flowers form on the shoot while it is alive.
Where does it grow from
The development of the flowering arrow occurs from the axil of the orchid leaf. Sometimes she looks out of the point of growth. Other shoots that emerge from the stem and other zones (root area) are children or roots. The arrow appears when re-flowering from a dormant bud of an old shoot. It grows away from the main stem and is characterized by weak bud formation.
The rapid development of the peduncle confirms the correctness of the care. Sometimes the arrow slows down development, and then turns yellow and dries up. The reason is insufficient supply of light and nutrition to the orchid.
Beginners are interested in how an orchid produces a flower stalk, and how long a new stem grows. Orchids bloom at different times in relation to their age. It is unlikely that a peduncle will appear from a young outlet. Some individuals bloom in the third year, others at an older age.
The duration of flowering depends on the species. Some varieties bloom all year round, despite the seasonality. Others at a certain time:
- Phalaenopsis blooms all year round, if the plant is properly looked after;
- Cymbidium - from October to the end of winter;
- Dendrobium blooms from mid-autumn until January.
The cultivation of an orchid is conditioned by the observance of the rules of care - the untimely watering causes the flowers to dry out together with the arrow. The lack of nutrients affects the length of the shoot. Peduncles develop well in diffused sunlight and high humidity. When buds are formed, feeding is stopped, otherwise the period of decorativeness of the flower is reduced.
Care before and after flowering
The appearance of a flowering arrow on an orchid is accompanied by compliance with the requirements:
- providing diffused lighting (avoiding the south side of the rooms);
- systematic watering of crops (when the top soil layer dries up);
- the location of the flowerpot with the orchid in a ventilated room, but without drafts;
- moistening the soil and air near the plant;
- regularity, complexity and usefulness of flower fertilization.
When the peduncle is formed, the conditions for keeping the orchid change. They concern:
- Locations. When a flower shoot is released in October, in spring or winter, move the container with the orchid to the south side of the room.At this time, the sun does not burn so much and will not harm the plant.
- Glaze. It is reduced little by little. Moisturize only once every 14 days (previously once a week).
- Make-up. With the appearance of a flower shoot, the frequency and amount of fertilization are reduced, but slightly. Growth and strengthening of the flower stem, swelling of the buds are the reasons for the end of dressing. Fertilization does not affect the number of flower buds. Their laying is carried out at the stage of flower shoot formation.
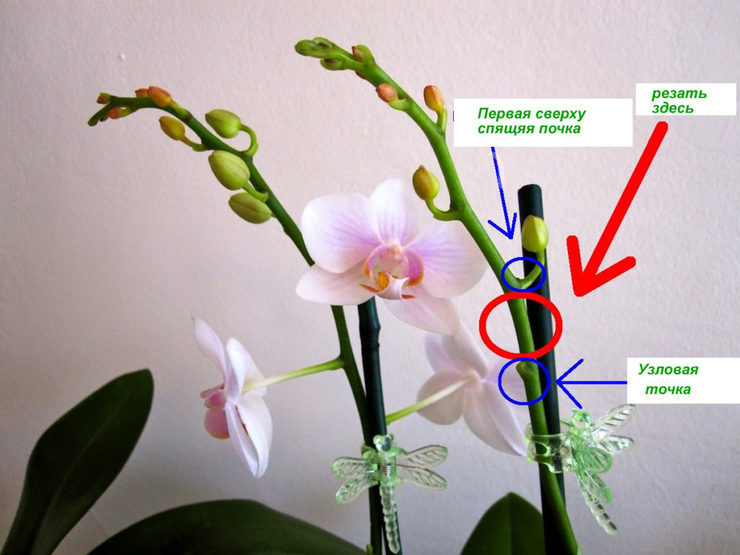
Is it possible to cut a peduncle
For several years, flowering arrows can produce flowers more than once. Other individuals fade and dry, giving way to new shoots. You should not rush to remove the peduncle that has immediately lost its decorative effect, despite its unpresentable appearance. While maintaining the green tone, the flower stem is not touched.
Signs will tell you whether it's time to remove the shoot:
- fast yellowness of a green peduncle or its acquisition of brown, red, purple colors;
- complete drying of the arrow;
- the green flowering arrow does not bud for 6 months.
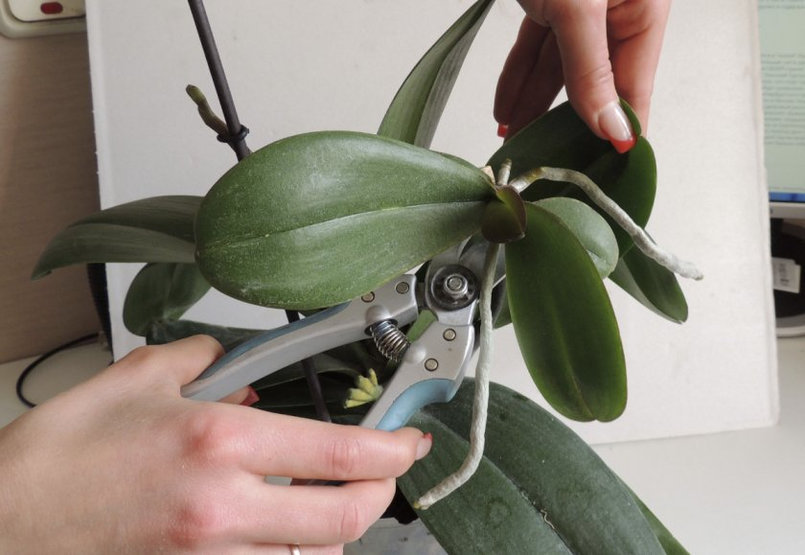
The flowering shoot needs to be cut off, a 3 cm shoot is left, which comes out of the leaf sinus. For cutting use:
- scissors;
- pruning shears;
- with a sharp knife.
The preferred tool is a pruner, which causes minimal damage to the orchid.
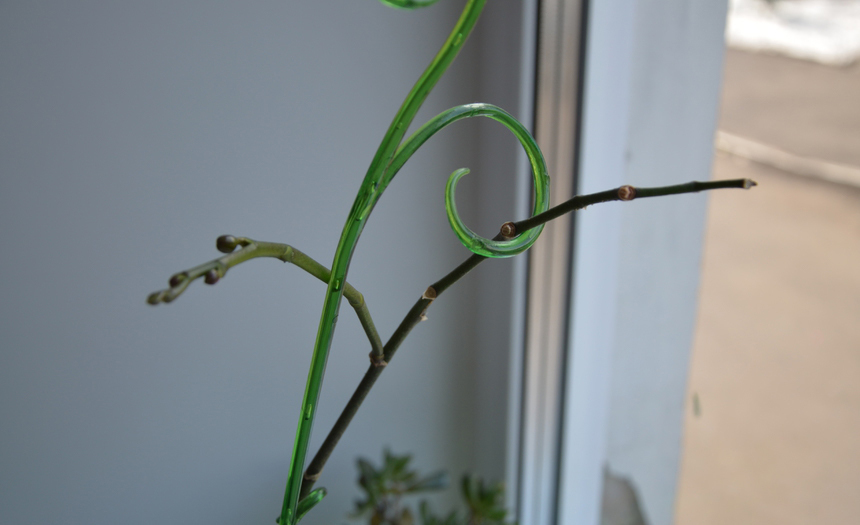
How to fix
To get an even stem, carry out the following manipulations:
- The garter of the flower is carried out vertically when it reaches 20 cm in height.
- The arrow needs to be fixed to the support. You will need an elastic band or a special clothespin.
- Correct the situation by overturning the flowerpot. The flowering shoot reaches for sunlight and straightens itself.
Possible problems
Yellowing
When the flower stem turns yellow and the shoots begin to dry out, pruning is carried out at the base. To prevent infection of the orchid, sprinkle the wound with ground cinnamon, crushed with coal. They also use chalk.
With a fading apical kidney, the arrow is made shorter. Cut off just above the first bud. The processing of open tissues is carried out with chalk along with cinnamon and charcoal.
Events develop in 2 directions: the termination of yellowing and the formation of a new flower stalk with buds on the hemp, or the disappearance of the peduncle and the formation of a new branch for the next year.
Desiccation
If an orchid has a dried peduncle, what to do worries flower growers. Often the drying of the peduncle is not a natural process.
It is generated by external reasons:
- Lighting. A lack of light leads to drying of peduncles, as well as foliage, air roots, buds, and slowing down of photosynthesis. The flower is threatened by the brightness of the light and the direct rays of the sun. It is preferable for the plant to have partial shade.
- Excess or lack of nutrients. The superfrequency of dressings negatively affects the orchid: the leaves, roots, peduncles dry out, the culture drops the buds. Lack of nutrition affects the slowdown or cessation of orchid growth.
- Air humidity. The deterioration of the state of the culture is observed under dry weather conditions due to unsatisfactory humidity. An excess of moisture leads to decay.
- Hypothermia. The temperature regime is at least +14 ° С. If the flower is supercooled, the peduncle wilts, the buds drop. The location of the culture under air conditioning and long airing of the room in winter is prohibited.
- Overheating of the root system. The plant likes warmth. However, it is not recommended to be under the scorching sun, near the radiators in the winter season and under the hot air flow from the working climate technology.
- Stress. Moving a flower to a new place causes shock due to changes in air humidity, temperature, light. The consequence is a suspension of development, shedding of buds.
Florists are interested in what to do if the stem of the orchid is withered.
To prevent negative consequences, it is advisable to leave the flower alone. The following manipulations are performed:
- lowering the temperature to + 20 ... + 22 ° С in the first weeks after cutting;
- reduction to a minimum of watering, but do not allow the casing layer to dry out;
- limiting the time spent in the light of the flower and excluding excessive illumination;
- maintenance of 50-60% air humidity;
- the regularity of airing the apartment;
- cessation of feeding the plant for a month after manipulation, after fertilizing once a month;
- periodic spraying with soft water heated to + 35 ... + 40 ° С.
Other
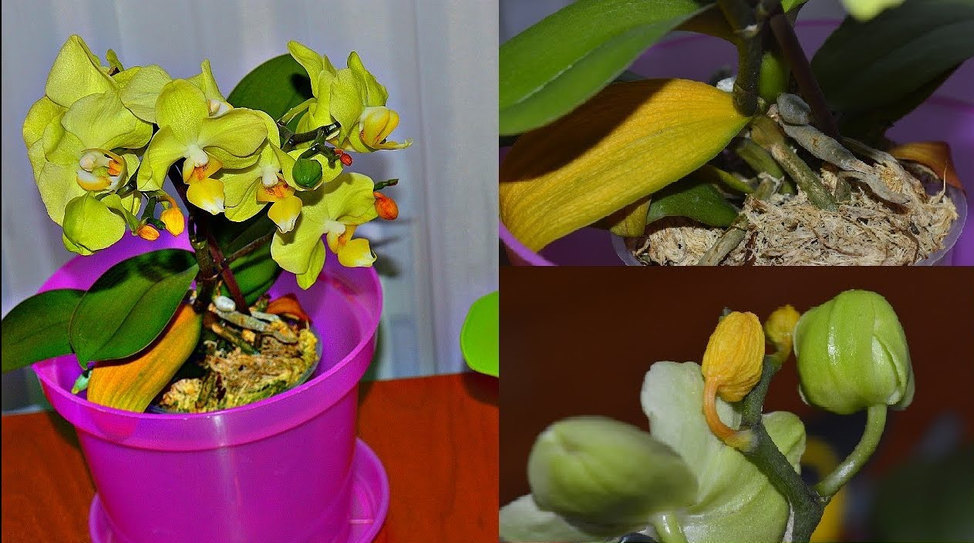
Leaves appeared on the stem of the orchid, what to do
Sometimes, instead of flowers, small paired leaves bloom on the shoot. This is a stem offspring or baby of a plant. The reason for this is the increased temperature (about +30 ° C), problems with the roots. The location of children on the arrow is not only single.
When babies are raised, a vessel with water is placed near the flower or sprayed daily 2-3 times. With the development of children, but weak root growth, they are wrapped in moistened moss. When the roots reach 5 cm in length, the children are separated from the mother's outlet and placed in separate pots. The cutting site is treated with charcoal.
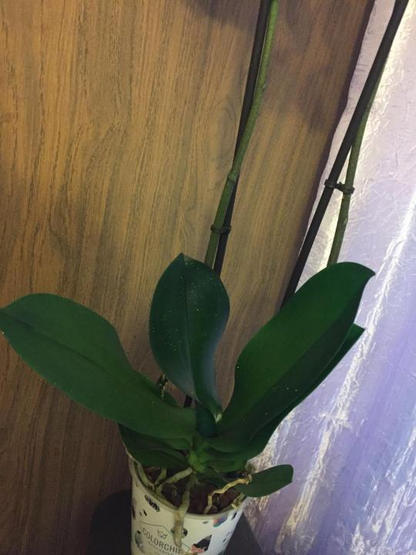
Peduncle formed, but does not develop
When a peduncle appears from the leaf axil, but growth stops, it is advisable to follow the conditions of the plant. Increase the intensity and frequency of watering. The flower needs nutrition, the plant is often moistened. Place the pot in the lightest spot in the room. Light affects the development of the peduncle. When no change occurs, the nutrient mix changes.
When the flower arrow breaks
If the stem is caught inadvertently, it can break. Cut off the flower shoot of a nearby bud at the site of the fracture. The cut is disinfected with an antiseptic. Soon a young shoot will form from the kidney.
Peduncle is absent
If Phalaenopsis does not have a peduncle, shock therapy is arranged. To activate the process, the flowerpot is transferred to a dark room. In addition, the amount of moisture is reduced, but the substrate does not dry out. It is desirable to lower the temperature in the room by 5 ° C at night. The method allows you to wake up Phalaenopsis sleeping for more than a year.
The peduncle of an orchid determines the development of the plant. He takes part in the cultivation of orchids. A full-fledged plant is grown from a torn off shoot. For the correct formation of the peduncle, it is important to adhere to the requirements for its cultivation. Their competent implementation will provide a beautiful flowering and aesthetic pleasure.